
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
||
Creating Ideal Trajectory for Immediate Implant
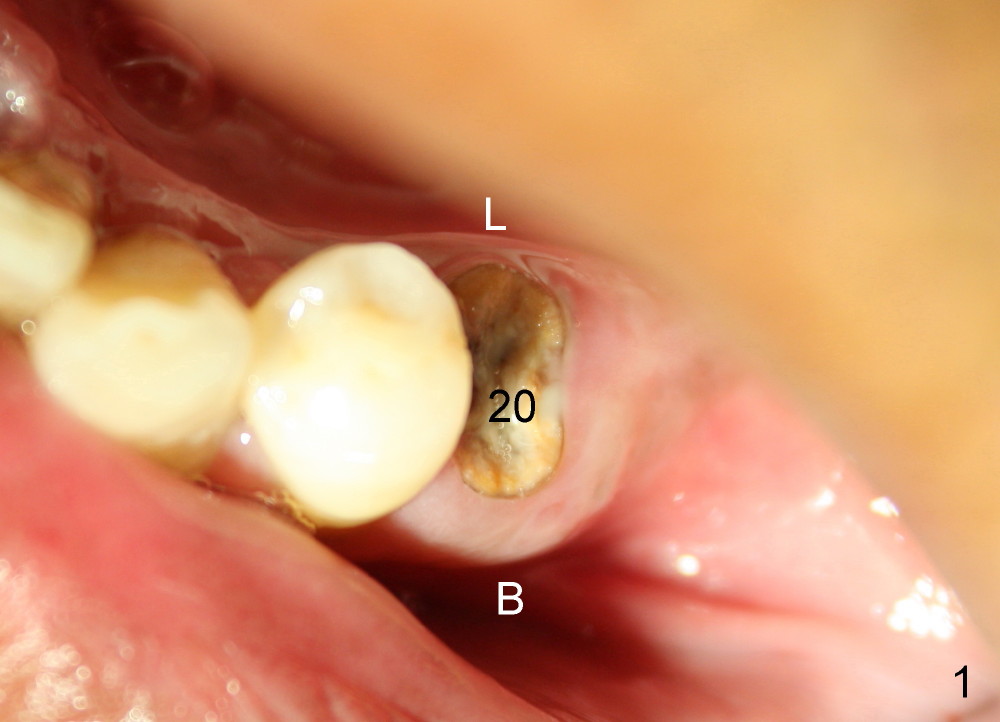
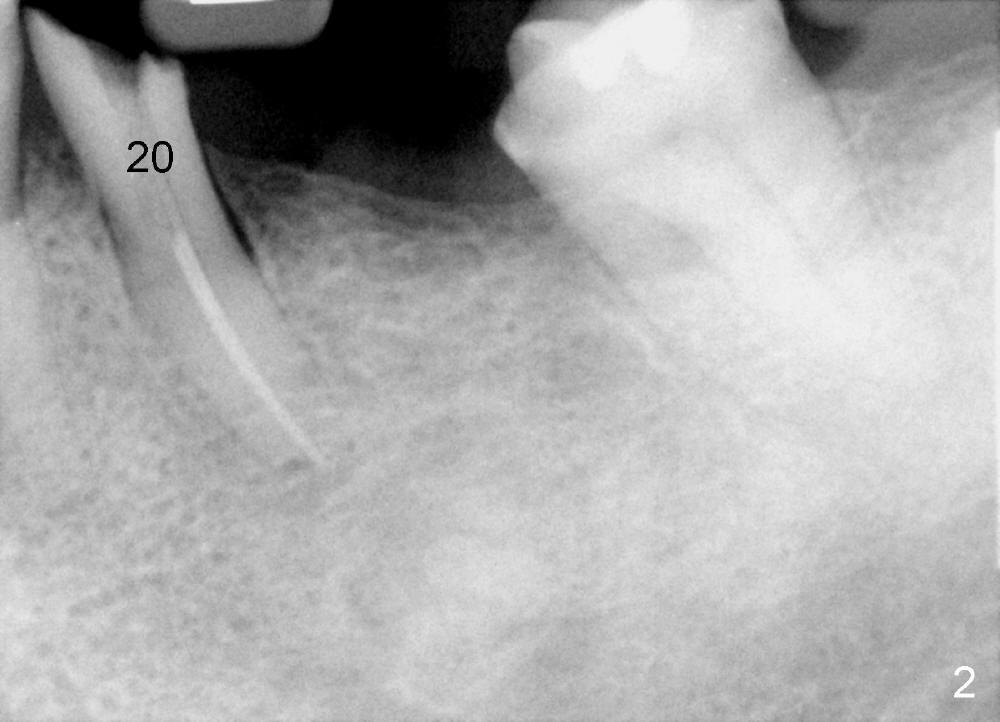
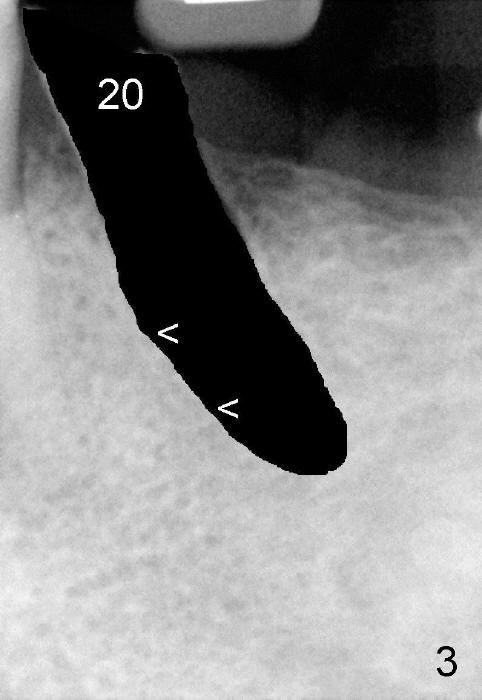
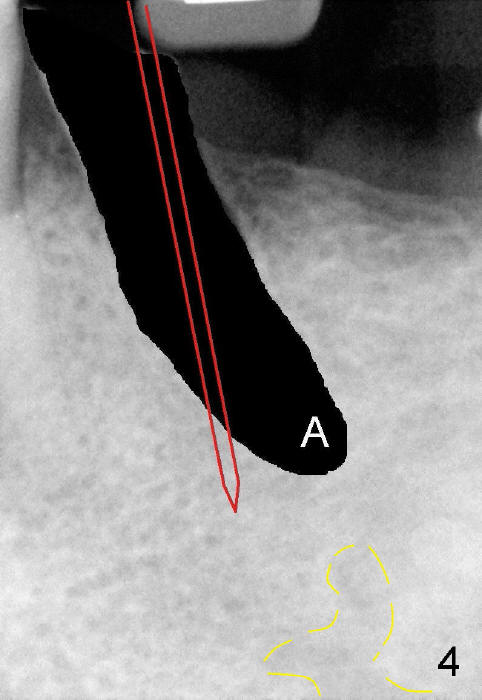
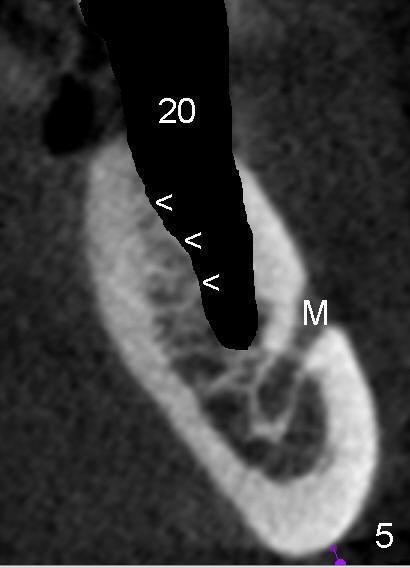
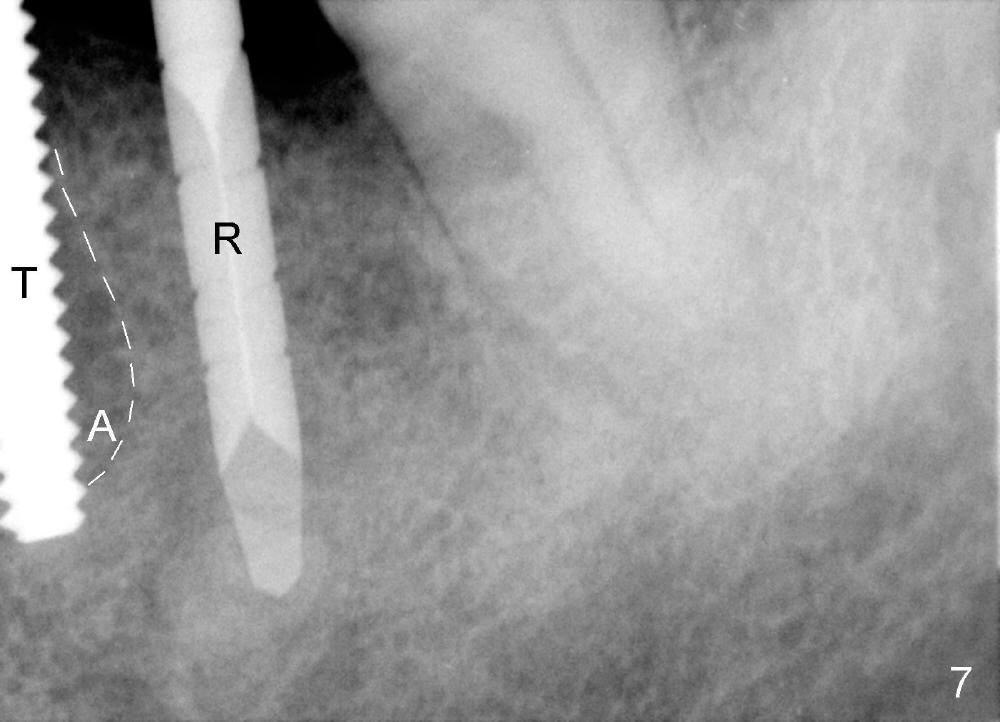
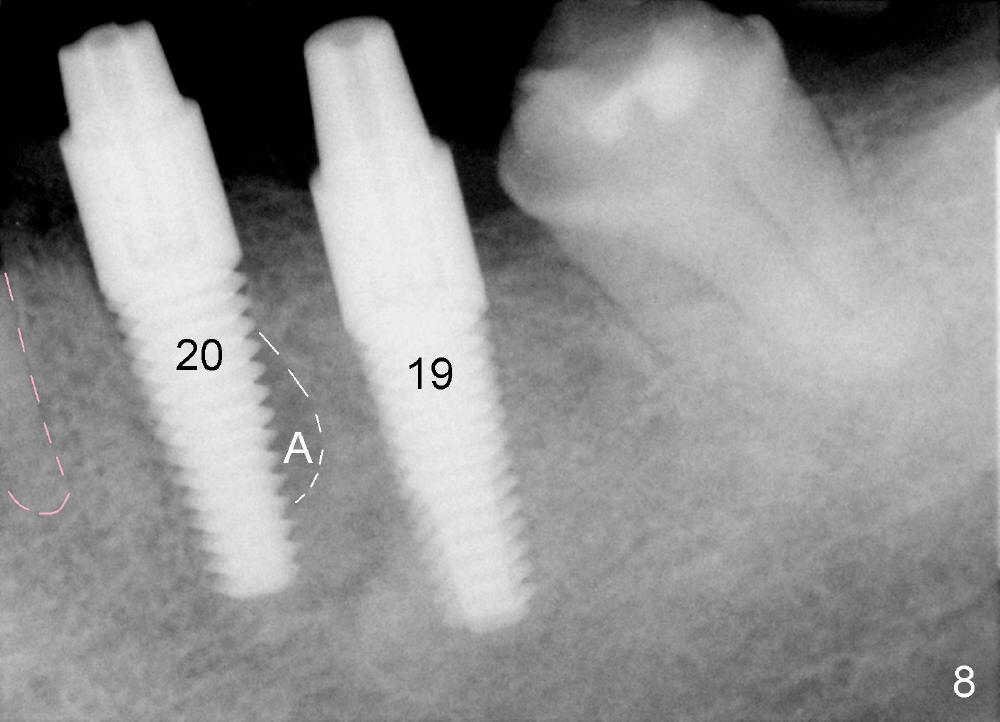
A 50-year-old man has lost a lower left fixed partial denture; one of the abutments (#20) fractures and appears to be non-salvageable (Fig.1,2). The root is dilacerated; when it is removed, there is a slope in the mesial aspect (Fig.3 <). Osteotomy starts in the mesial slope (Fig.4 red pointed rod (pilot drill)). The intermediate (Fig.7 T (tap)) and final (Fig.8: #20 (implant)) trajectory seems to be more ideal than that of the natural tooth. A in Fig.4-6 stands for the apex of the original socket. In addition, the apex of the osteotomy is relatively deviated from the mental loop (Fig.4 yellow outline).
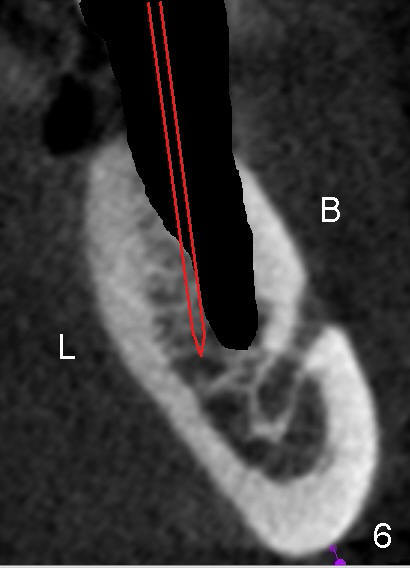
When the 2nd premolar is extracted, the lingual plate (L) is found thicker than the buccal (B); osteotomy (Fig.6 (not the same case) red outline) forms in the lingual slope of the socket (Fig.5 <) instead of being along the original longitudinal axis. The new trajectory in this direction is also safe for the mental loop (M).
In the 3 dimensional socket, the osteotomy is formed in the mesiolingual slope.
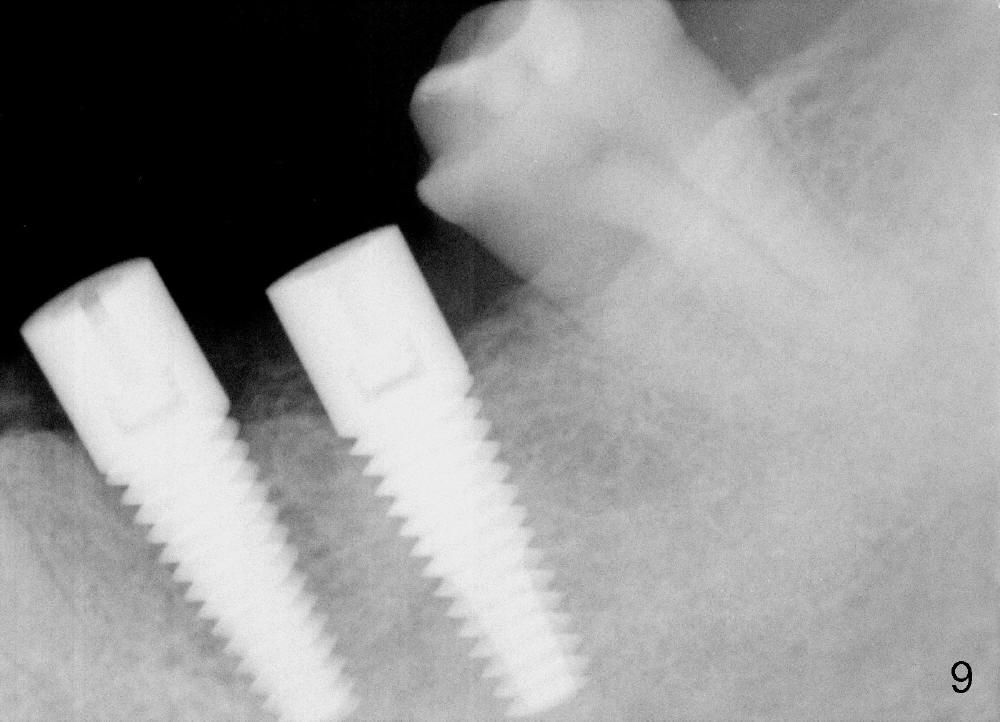
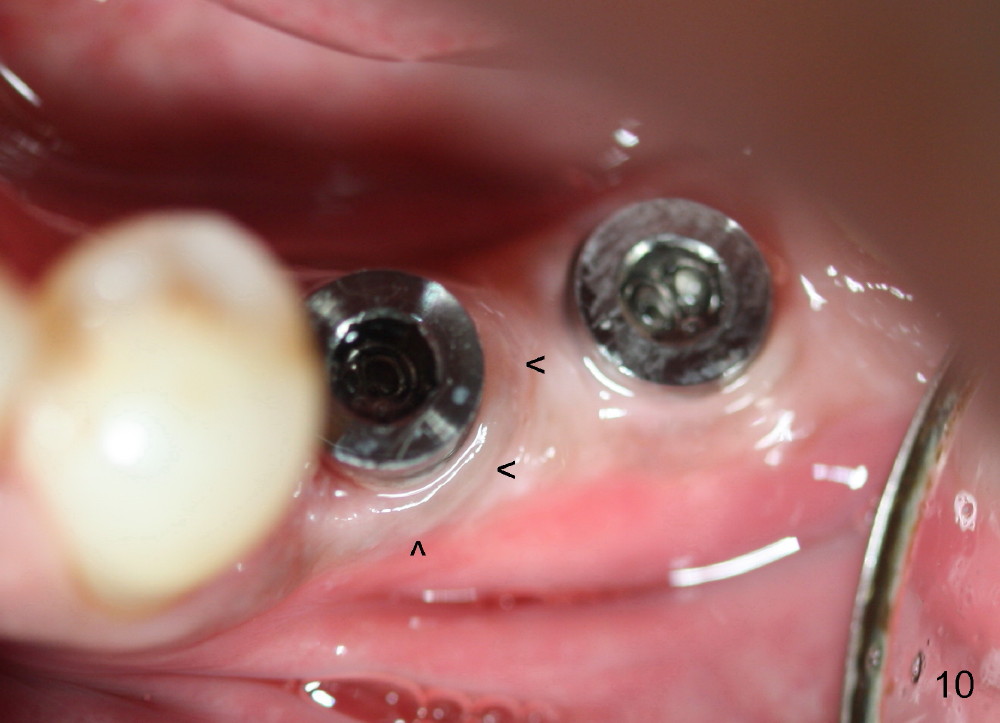
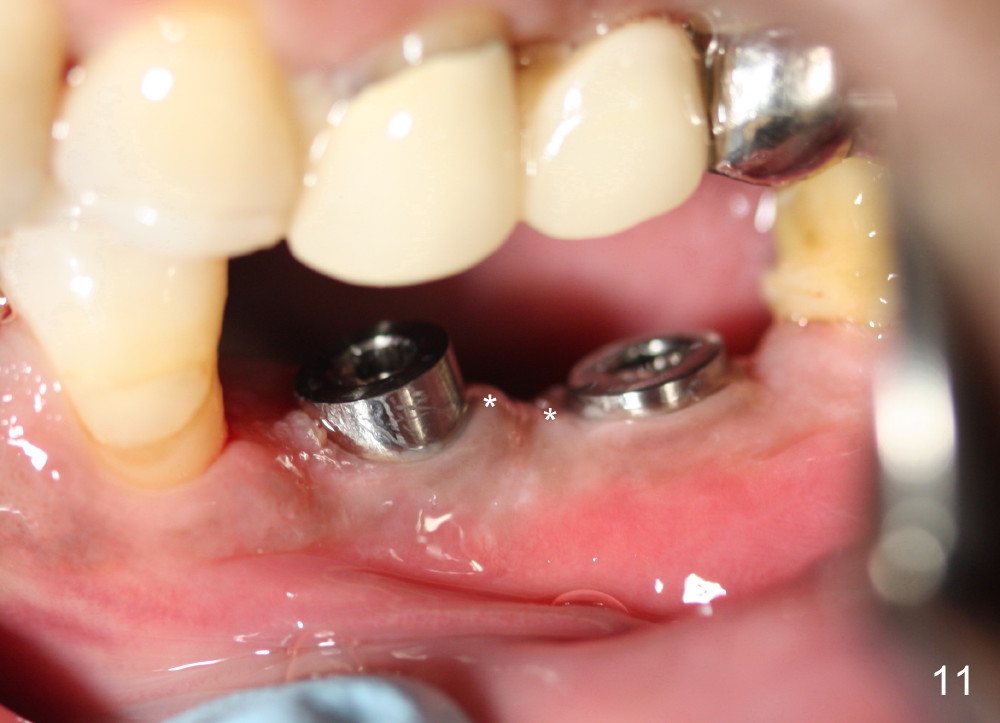
Five months postop, the extent of the original apex of the socket at the site of #20 decreases (Fig.9). The gingiva forms a cuff around each implant (Fig.10 arrowheads). The cuff around the immediate implant is higher than that of the delayed one (Fig.11 *).
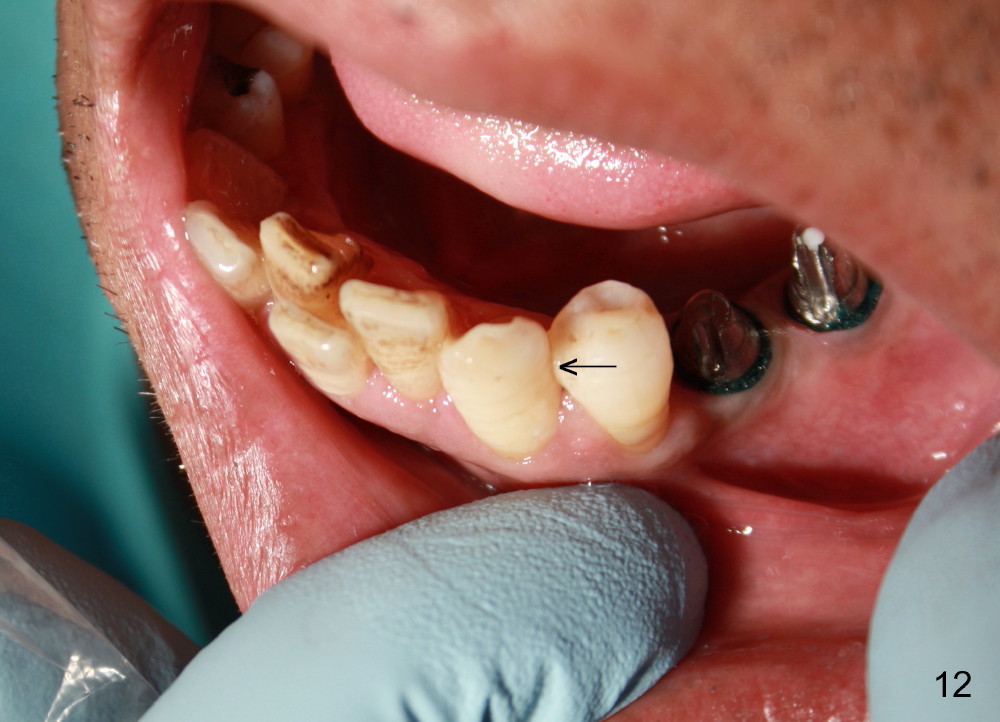
The abnormal existing long axis of the premolars is probably related to anterior crowding (Fig.12). The roots of the premolars remains in the original place, while the crowns shift anterior (arrow). Therefore, it is justifiable to change the trajectory when the implant is placed.
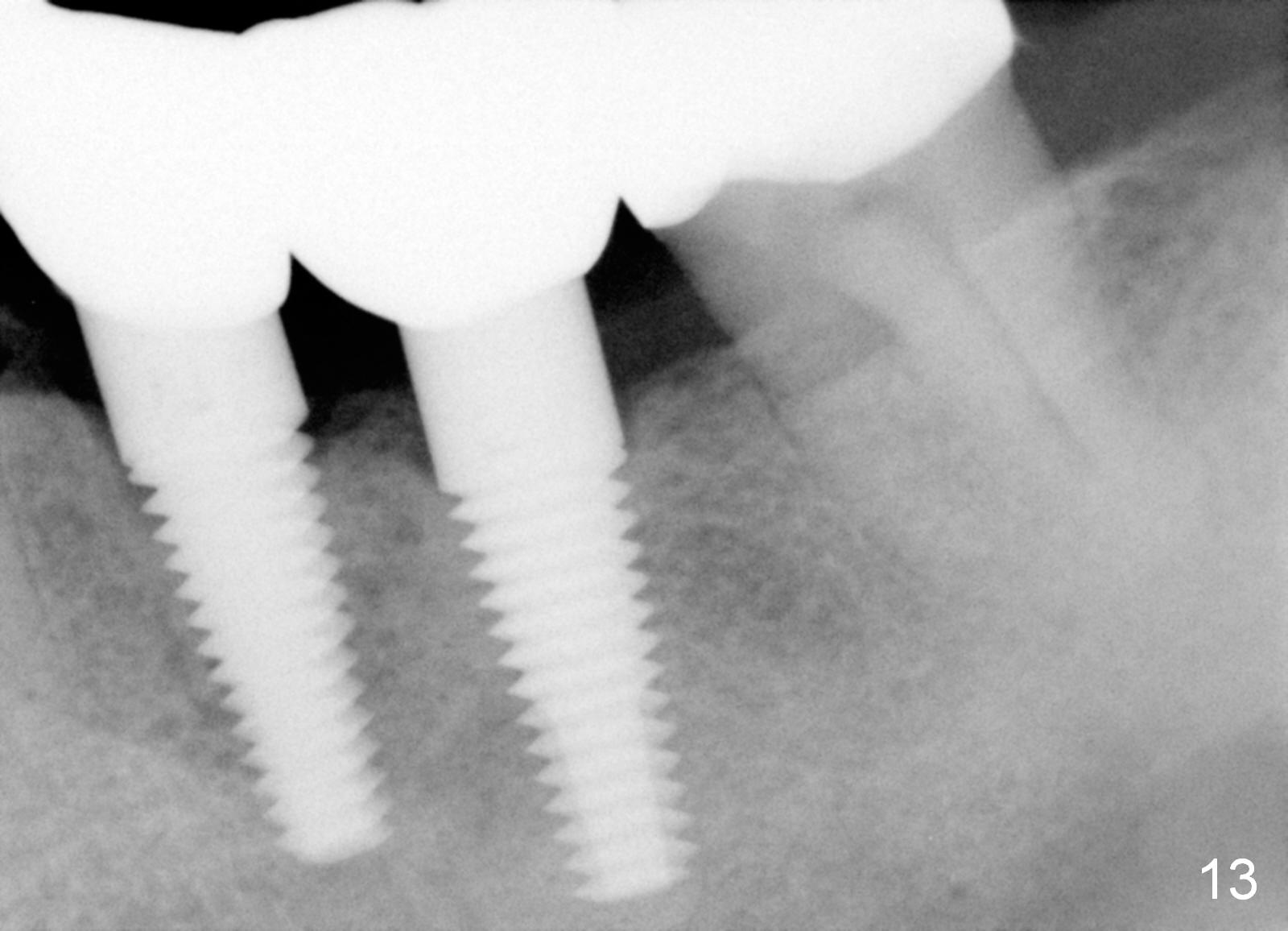
There is mild crestal bone resorption distal to the implant at the site of #20 five (Fig.9) and 12 (Fig.13) months postop. It may be related to the change in the trajectory.
This case of the immediate implant is not immediately provisionalized. There are two drawbacks. It takes 11 months to cement the implant crowns. Patients tend to delay definitive restoration if not immediately provisionalized. Immediate provisionalization may reduce occlusal reduction of the tooth #18. There is sensitivity after the crown repreparation.
Thirteen months post cementation (20 months postop post cementation), the patient returns because of #18 chewing pain. Dense bone forms around the coronal portion of the implants (Fig.14 *).
Return to Lower Bicuspid Immediate
Implant,
Dr. Wu,
Posterior Immediate Provisional
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 07/22/2014, last revision 01/19/2018